Calling Rust from Excel
This post is part of a series on interfacing Excel with various programming languages.
Excel
Excel is a tool that appears to be as loved as it is hated. Personally, I think its a fantastic tool, however its main benefits (easy to pick up and understand) also mean it is often used for tasks when it is no longer suitable, I have heard many a horror story of files taking minutes to load and requiring hours of pain staking checks just to make simple change due to their complexity.
Whatever your opinion of Excel, it is a tool many people are familiar with and can be used as a useful UI for certain types of applications. In this post I will demonstrate how to call Rust code from Excel via C#.
Update: I rebuilt the project below in late 2022 using Rust 2021 edition, Visual Studio 2022 and ExcelDNA 1.6 and it all worked as expected. Just ensure you select .Net Framework when creating the class library and dont use i586-pc-windows-msvc unless you are targeting a 32-bit version of Excel.
Rust
I am going to assume you have Rust installed and know how to use Cargo to create and build projects. If not please follow the instructions on the RustUp website to install Rust.
I have also covered calling Rust from other languages (Python, R) here and if you are new to Rust please read that also.
Excel-DNA
Excel-DNA is a .Net library that provides a high level API for interacting with Excel. Excel-DNA can be used to create both UDFs (functions you can call from a formula) and custom ribbon interfaces.
For this project we will write the algorithm in Rust, and call it from Excel via C# and the Excel-DNA API. I have two previous posts showing how to used Excel-DNA with F#, Part 1 and Part 2. Reading those will help you get familiar with Excel-DNA.
Set up and Simple UDF
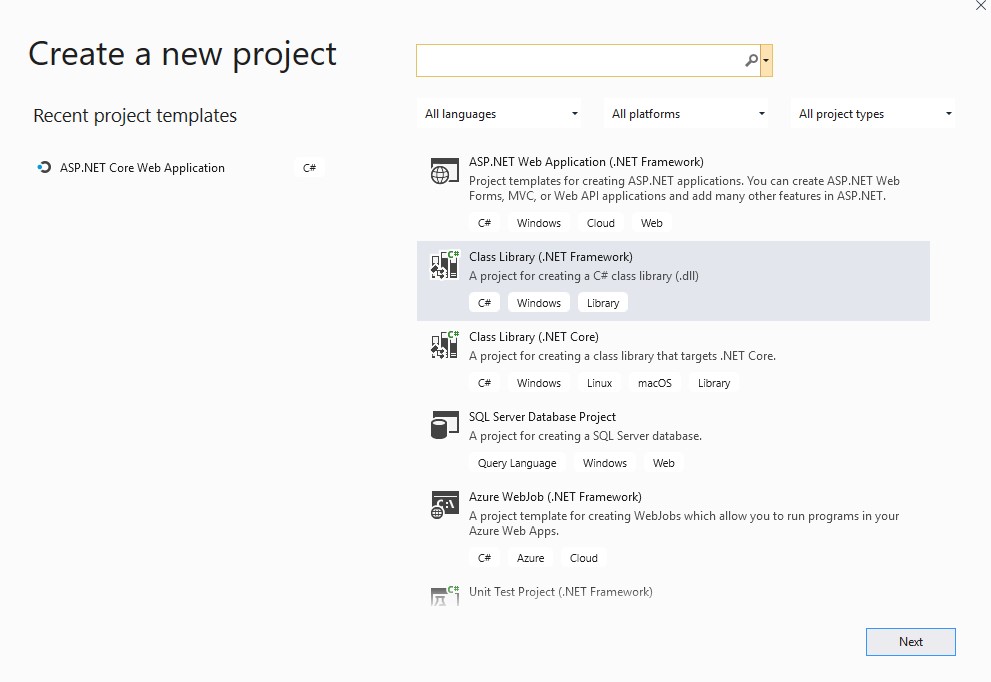
In Visual Studio create a new Class Library (.NET Framework) and call it RustExcel.
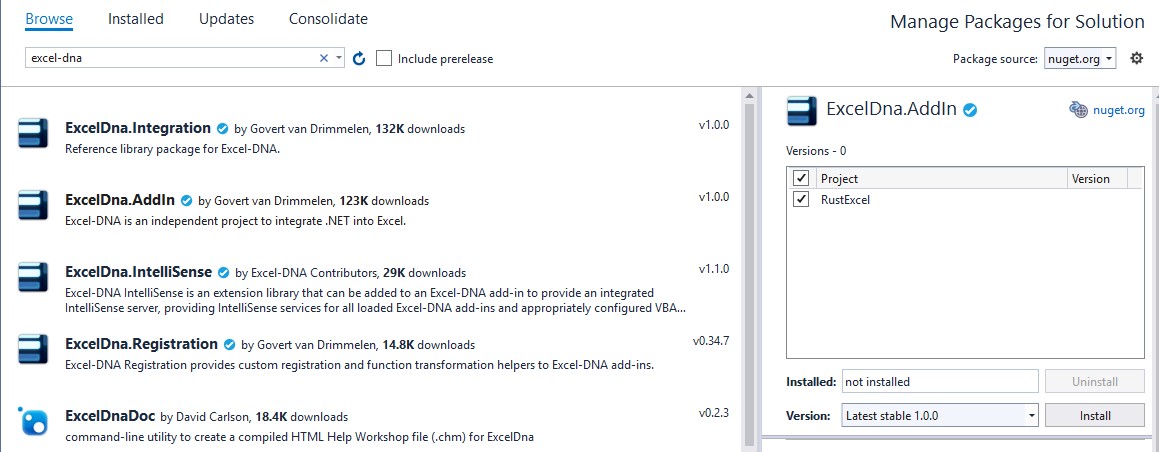
Next, use the NuGet Package manager to install the Excel-DNA package.
Finally, rename the Class1.cs file to something more sensible such as Functions.cs and add the following
using ExcelDna.Integration;
public static class Functions
{
[ExcelFunction(Description = "Return the sum of two numbers")]
public static double RustSum(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
Set up the projects debugging settings as described previously and hit F5. Excel should open and you should be able to use the function you have just defined.
Create Rust Project
As you will often have to deal with older 32 bit versions of Excel, we will build our library as 32 bit. Add the following target using rustup:
$ rustup target add i586-pc-windows-msvc
Now create a new Rust library project
$ cargo new rustlib --lib
And modify the build file to create a dynamic library.
[package]
name = "rustlib"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Jonathan Harrington <--->"]
edition = "2018"
[lib]
name="rustlib"
crate-type = ["dylib"]
[dependencies]
Next, create a cargo config file in .cargo\config and add the following:
[build]
target = "i586-pc-windows-msvc"
Finally, open lib.rs and add the following:
#[no_mangle]
pub extern fn add_numbers(number1: f64, number2: f64) -> f64 {
number1 + number2
}
Now if you run cargo build you should now have a 32 bit rustlib.dll in your output folder (target\i586-pc-windows-msvc\debug).
Note: If the build fails make sure you have installed the Microsoft C/C++ toolchain as part of your Visual Studio install.
Calling Rust from Excel
Now back in our C# project we need to add the dll to our project. Right click on the project and select Add -> Existing Item and browse to the rustlib.dll in target\i586-pc-windows-msvc\debug.
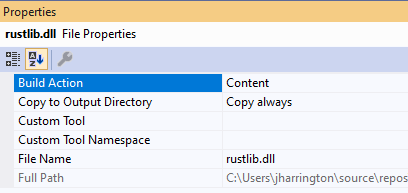
Then modify the file properties to ensure it is copied to the output directory. Finally, change the code in Functions.cs to the following:
using ExcelDna.Integration;
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
public static class Functions
{
[DllImport("rustlib.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
private static extern Double add_numbers(Double number1, Double number2);
[ExcelFunction(Description = "Return the sum of two numbers")]
public static double RustSum(double a, double b)
{
return add_numbers(a, b);
}
}
Here we use the .NET Pinvoke functionality to declare the rust functions as external and then we simply call it from our C# wrapper. Now when you hit F5 and load Excel you can call “RustSum” as a UDF.
Conclusion
Excel-DNA makes it very easy to create Excel Add-ins and Rusts (and C#s) excellent FFI support allows for easy interop with C#. Shout out to dev.to and jakegoulding.com for creating some great easy to follow content on this. You should go read their sites for more info.